
[ad_1]
Prysmatic Labs, a team of blockchain engineers committed to downsizing Ethereum, recently released a development update for the open source sharding client for Ethereum 2.0 Casper.
This week's update is a follow-up to their previous update dealing with cross-shard communications inefficiencies. The team faced the canonical "Hotel and train problem" that occurs in cross-shard communications. As explained by Raul Jordan, a developer of Prysmatic Labs in one of his last interviews:
"[Hotel and train problem] which is that if you book a train and book a hotel, you want both to pass or none. Hotel, but not your train or the train that passes and you're not a hotel. "
Applying the same in the context of Ethereum, the developer further explained, if there exists Transaction A who lives on a fragment and depends on the finalization of another Transaction B, which resides on another fragment, with different latencies, different parameters, different types of nodes that cross over them, there is a possibility that the whole system will fail if you it goes through and the other does not. He also added that someone's account on the network could end up receiving more Ether than what he owns. The whole scenario can create a big problem across the chain, he explained.
In their previous report, the team also discussed how the aforementioned problem could be solved using the concept of "shark contract tear" explained by Vitalik Buterin in one of his recent postings on sharding research

Vitalik Buterin proposal of the cross-quartering contract | Source: Ethereum official research page
However, in its current report, the team also stated that the "cross-squaring contract" was imperfect in terms of accommodating latencies. The team was trying to offer cross-shard communications in one transaction. As a solution, they examined Vitalik Buterin's latest sharding research entitled "Simple synchronous cross-shard".
In his post, Buterin explains that to get a single cross-shard communication transaction, it requires data and state separation due to the possibility of reorg [block reorganizations].
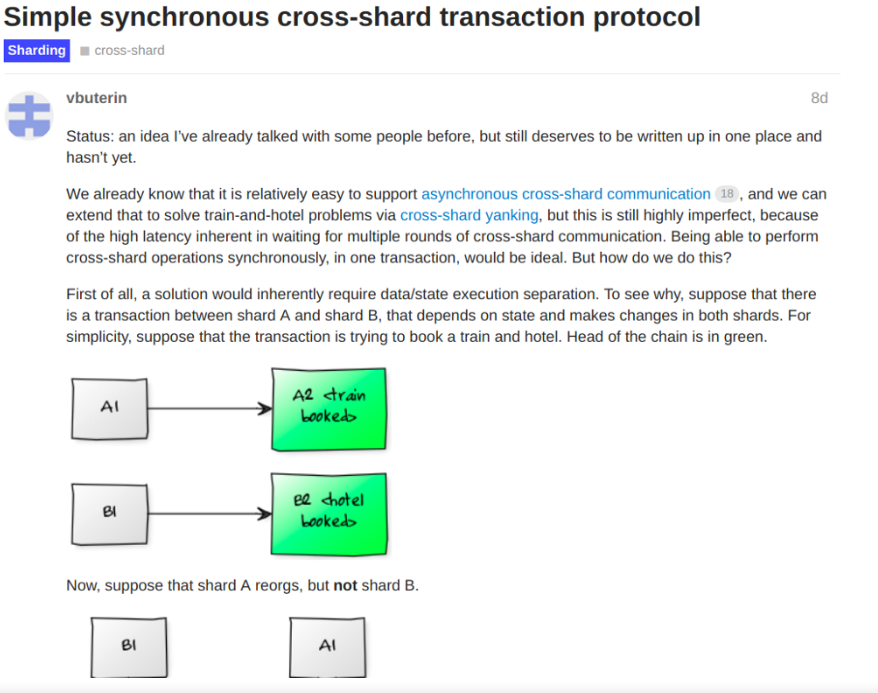
Buterin: simple synchronous cross-shard transaction protocol | Source: Ethereum's official research page
Discussing Vitalik Buterin's recent take on Level 2 solutions, the team said:
"At Prysmatic Labs, we are right at the crossroads of all these important considerations. a mission within our team to build a robust Ethereum progression protocol that can last over time. "
In the next section of the paper, the team briefly explained GitHub pull requests, merging codes and problems that have been addressed or will be addressed in the future. The team has successfully aligned the codebase with its latest 2.1 specifications. The team continued to work out how it developed a solution for the Beacon nodes for bootstrap from a genesis state.
Beacon nodes are random sidechains developed by the Prysmatic Lab team that stores hashes on the main chain blocks in their blocks. According to them, this sidechain will be a complete "Proof of Stake" system that will implement Casper FFG and provide a source of distributed randomness that will allow the team to build a sharding system on it.
In the next section, the team stated that a DAG [Direct Acyclic Graph] will store information about incoming blocks and their status. Furthermore, as an improvement, one of the team members introduced a solution that made the system simple for memory requirements. The report said:
"Nishant Das of our team then took the initiative to improve the system and instead to store all incoming blocks processed in persistent storage and to keep only a simple portion of memory blocks in memory that we have yet to process for the last number of slots and then easily apply the rule of choice of the fork. "
The team also revealed that new and exciting developments are pending implementation in the specific beacon chain v2. 1. The team also integrated a functionality within the beacon nodes to allow it to save blocks and states in the database.
The upcoming work of the team includes the implementation of an interaction of the Peer to Peer message [P2P] among the Validators [Proposers/Attestors] to exchange information. In addition, they will also work to advance the Beacon chain from Genesis without the use of a simulator. They said:
"Currently, we have a simple simulator that transmits false blocks and tests to test the development of the beacon chain for development purposes.To arrive at a meaningful demonstration, we want the chain to advance correctly through actual proposals and claims from the genesis using a beacon node and a validator client connected via RPC. "
Source link