
[ad_1]
Credit: Wiley
Metal ion hybrid capacitors combine the properties of capacitors and batteries. One electrode uses the capacitive mechanism, the other the battery-powered redox process. Scientists have now examined the role of anions in the electrolyte. The results, which were published in the journal Applied chemistry, reveal the importance of sulfate anions. Sulfate-based electrolytes have provided the zinc-ion hybrid capacitors with outstanding performance and extra-long run time.
Capacitors can absorb and release a huge amount of charge in a short time, while batteries can store a lot of energy in a small volume. To combine both properties, scientists are studying hybrid electrochemical cells, which contain both capacitor and battery-operated electrodes. Among these cells, the researchers identified metal-ion hybrid capacitors as particularly promising devices. Here, the positive electrode includes pseudocapacitive properties, which means it can also store energy in the manner of a battery by intercalating metal ions, while the negative electrode is made up of a redox-active metal.
However, their electrolyte has long been overlooked, says Chunyi Zhi who is studying battery materials alongside her team at City University of Hong Kong. Researchers believe that the type of electrolytic anion affects the performance of the device. “Paying more attention to introducing appropriate anions can actually improve a capacitor’s power and energy density,” they say.
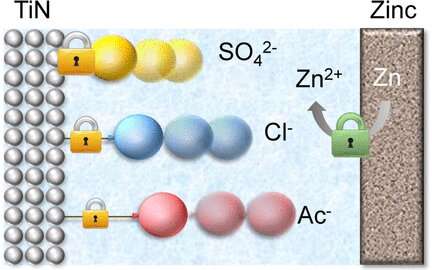
The researchers focused their attention on zinc ion capacitors. This type of cell consists of a zinc metal anode and a titanium nitride nanofiber cathode. The nanofibers are robust and their porous surface allows the electrolyte to infiltrate. Scientists claim that electrolyte anions, when attached to the surface of the titanium nitride, make the material more conductive. Furthermore, the adsorbed anions can directly contribute to the charging process. Charging the hybrid capacitor involves the extraction of the intercalated zinc ions.
Zhi and his colleagues compared the effects of three electrolyte anions: sulfate, acetate and chloride. They examined both their bond with the electrode surface and the performance of the electrochemical cells. It was a clear result.
Scientists reported that sulfate anions stood out among the three anions. They observed that cells based on a zinc sulfate electrolyte performed better and that the sulfates bonded more strongly to the surface of the titanium nitride than the other anions. Additionally, sulfate-treated electrodes exhibited the lowest self-discharge. The authors attributed the results to the electronic effects of the sulfate. Its electron-attracting nature provides a close bond with the surface atoms and prevents the electrode from self-discharging, the authors concluded.
For a zinc-ion-zinc sulfate-based hybrid capacitor, scientists reported high-performance operation for more than nine months. Additionally, these devices are flexible, which is especially useful for portable electronics. Scientists tested the device in an electronic watch and found excellent performance.
The reorganization of solvation brings stable zinc / graphite batteries closer to storage in the commercial network
Zhaodong Huang et al. Effects of anion carriers on the capacitance and self-discharge behavior of zinc ion capacitors, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2020). DOI: 10.1002 / anie.202012202
Quote: Zinc Ion Hybrid Capacitors with Ideal Anions in Electrolyte Show Extra Long Performance (2020, November 13) recovered November 13, 2020 from https://phys.org/news/2020-11-zinc-ion-hybrid -capacitors- ideal-anions.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any conduct that is correct for private study or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.
[ad_2]
Source link