
[ad_1]
FP trendNovember 16, 2020 15:17:57 IST
Scientists have now found that water vapor near the surface of the Red Planet is being sent higher into the atmosphere than was previously thought possible. Once there, it is destroyed by electrically charged gas particles or ions and is lost in space. They found this out using NASA’s Mars Atmospheric and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) probe.
According to a declaration Released by NASA, the researchers said the phenomenon they discovered is the reason why Mars has lost the equivalent of a global ocean of water up to hundreds of feet deep in billions of years. They added that Mars continues to lose water today as vapor is carried to high altitudes after sublimation from the ice caps during warmer seasons.
Sublimation is the passage of a substance directly from the solid to the gaseous state, without passing through the liquid state.

Image: Pixabay
Study author Shane Stone said they were all surprised to find water so high in the atmosphere, adding, “The measurements we used could only come from MAVEN as it flies through Mars’ atmosphere, high above the surface. of the planet “.
Stone and his colleagues based their findings on data from MAVEN’s Neutral Gas and Ion Mass Spectrometer (NGIMS). The mass spectrometer essentially inhales the air and separates the ions that make it up based on their mass.
Researchers have monitored the abundance of water ions on Mars for more than two Martian years and determined that the amount of water vapor near the tip of the atmosphere about 150 kilometers above the surface is highest during the summer in the southern hemisphere. During this time, the planet is closer to the Sun and therefore is warmer and sandstorms are more likely to occur.
The hot summer temperatures and strong winds associated with dust storms help water vapor reach the higher parts of the atmosphere where it is broken down into hydrogen and oxygen which escapes into space.
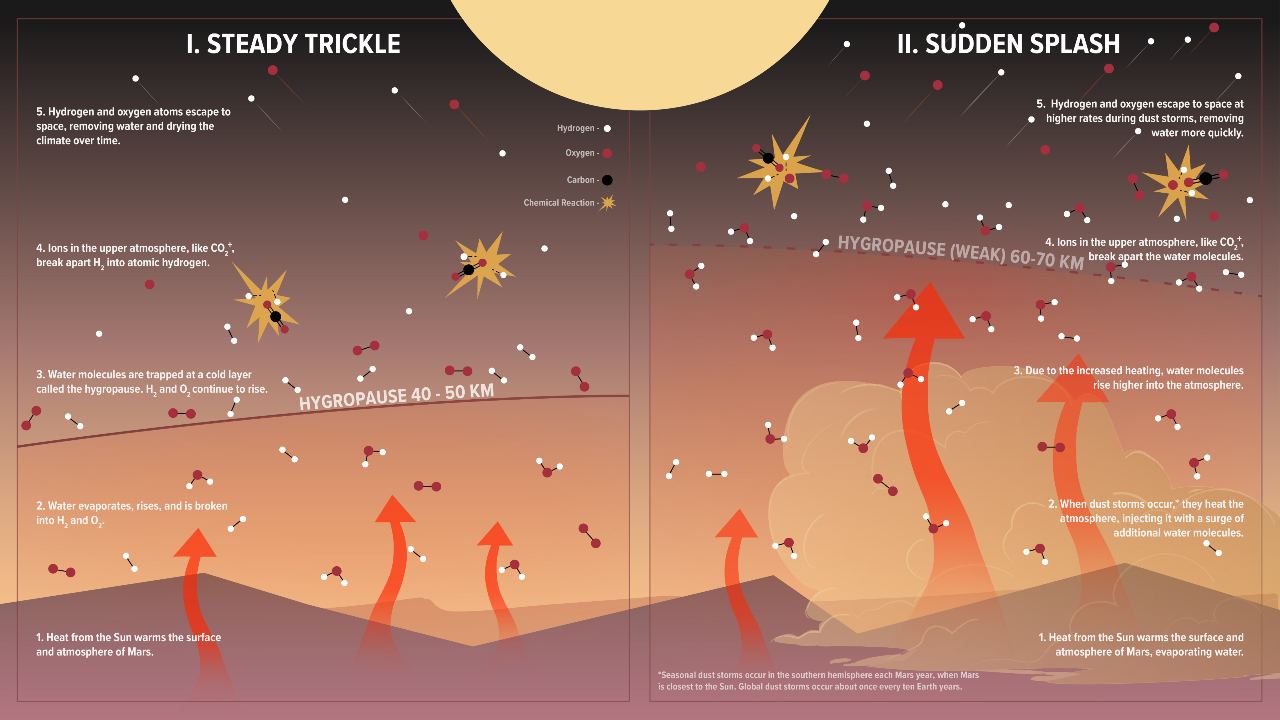
This illustration shows how water is normally lost on Mars compared to regional or global dust storms. Image credits: NASA / Goddard / CI Lab / Adriana Manrique Gutierrez / Krystofer Kim
Stone added that anything that reaches the top of the atmosphere is destroyed on both Mars and Earth as it is exposed to the full force of the Sun.
Paul Mahaffy, principal investigator at NGIMS, added that they have shown that dust storms disrupt the water cycle on Mars and push water molecules higher into the atmosphere where chemical reactions can release hydrogen atoms into space. .
Mehdi Benna, co-author of the study, added that what is unique about the discovery is that it provides a new path they didn’t think existed for water to escape the Martian environment. The researchers believe the discovery will change their estimates of how quickly the water escapes in the present and how fast it has escaped in the past.
.
[ad_2]
Source link