 [ad_1]
[ad_1]
The blockchain currently stores many types of transaction information such as transfer information from A to B, temporary information and other information that temporarily takes up ample space because there is no other place to store it. Commercial blockchain applications involve not only transactions, but also the logic of the business system that requires more abundant data, such as resource text data, numeric data, multimedia video data, etc., which are not stored on the blockchain.
Popular blockchain storage projects
Both is the first bitcoin storage-based storage solution. Storj is similar to Sia as it extracts data from a network disk. It does not provide any storage space accessible to programs. The way to demonstrate data integrity is to make sure that the customer and the filing party sign a contract. Both sides will probably be in this situation. It is expected that cheating provides evidence of data storage.
The project of the protocol laboratory initially created the open source software InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), which is positioned as the infrastructure of the new transport protocol. The IPFS network is similar to the existing P2P network ten years ago, like eDonkey and Thunder. There is no incentive mechanism for the IPFS network, so the postprotocol laboratory has launched a new project called Filecoin to provide decentralized storage incentives.
Lambda, however, is a storage solution accessible to the program. Its underlying protocols use a basic file system with object storage, Key-Value storage (KV), and other types of storage. It can be extended to provide more complex relational storage.
Filecoin uses a more mature IPFS network. On this basis, the incentives will imply the consent of the blockchain. Those who contribute the most will be rewarded more and are imperative to prevent cheating. The most important thing in the blockchain space is that all participants can benefit from it and the benefits are directly proportional to the effort made. The blockchain is an economic model, not just a technical model.
The two most important points of Filecoin are copy-proof and space-time. Filecoin started writing his white paper in 2014 and the consensus at the time was Bitcoin's Proof of Work (POW). Thus, in 2014, Filecoin focused on creating innovative consent algorithms and their storage hooks that guide technical solutions.
Fundamental technological concepts in the Blockchain storage arena
The first is Provable Data Possession (PDP), which is not commercially available. Only cloud storage companies use PDPs, but there is no mechanism that allows users to try out data storage based on customer needs. The algorithm was used in the field of decentralized storage and the technology developed very quickly.
The second is the Recovery Test (POR), which is similar to the PDP and is more forgiving. A redundant backup is provided and the storage space does not increase linearly based on the number of copies. At the same time, at a certain fault tolerance level, when some data segments are lost, the data can be restored to other sectors.
Finally, the Erasure Code (EC) technology, which is similar to hardware RAID technology in traditional storage. These three technologies are key technologies for decentralized storage.
Proof of data integrity for blockchain storage solutions is a central problem that requires a solution. However, there is no complete solution at this time. The integrity of decentralized storage turns out to be as complicated as blockchain information. While data is present in the miner node, a corresponding mechanism is needed to detect if the node stores data.
Protocols used by different archiving projects
Filecoin's consent mechanism is Proof of Storage (POS), in which S is not a currency interest, but rather how much time and how much data the miner has helped clients. Storage is one of the most critical factors affecting consent, so Filecoin adds a number of additional anti-cheating rules to the archiving certificate; this increases exponentially the difficulty of technical implementation. Furthermore, it is not very helpful in the POS as it contributes to the fairness of consent.
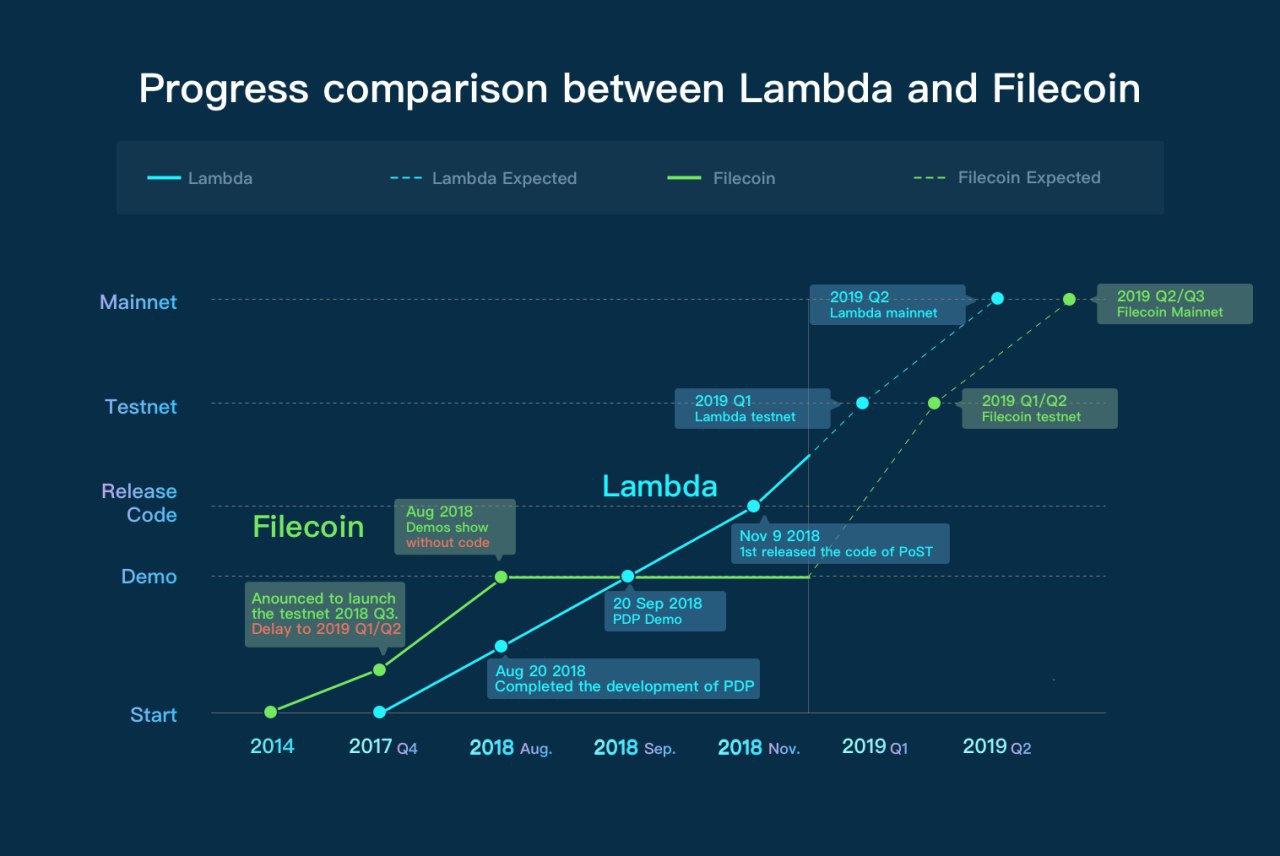
In a recent research study conducted between Filecoin and Lambda, the data points show a significant plateau in the development of the Filecoin project while Lambda's growth in particular in 2018. The graph examines the launch of Lambda and Filecoin, a code test of success, project development and expected growth in 2019. Both companies are expected to launch their main network in the second quarter of 2019, Lambda continuously shows steady growth and progress while Filecoin is lagging behind and currently shows no improvement.
For the first time, Lambda provides the concept of a verification node in the field of decentralized storage. This is similar to the idea of the third-party administrator (TPA) mentioned in academic research. Instead of using a TPA node, Lambda created the 1024 Validator position on the consent network and used the Verifiable Random Function (VRF) consent mechanism to achieve a verification result for the archiving test, avoiding the high risk of mutual cheating from both storage and verification nodes. In addition, Lambda separates storage from its chain, which is more conducive to upgrading and developing storage technology. The evolution of storage does not affect transactions on the chain and is more conducive to the development and expansion of the capacity of the Lambda ecosystem.
Lambda fully implements PDP, POR and EC technology, which significantly enhances the security of decentralized storage. It also optimizes the storage space and traffic consumed by the algorithm to achieve the same level of secure storage. Lambda decentralized storage enables safer storage at a lower cost. A small step in Lambda storage technology is a big step in the development of the blockchain infrastructure.
While each project has its merits, the goal is always to use unique protocols that provide solid storage capacity. Recently, Ethereum World News reported on the launch of Lambda's Proof-of-Space-Time verification that addresses many of the existing limits in the PDP algorithm.
Image courtesy of Shutterstock and Lambda.