[ad_1]
A recent study published on the prepress server bioRxiv* in October 2020 reports the development of a new vaccine based on a simian adenoviral vector obtained from a group C gorilla isolate called GRAd32. This could help accelerate vaccine development.
Low seroprevalence for simian adenoviruses
Monkey adenoviruses are isolated from non-human primates such as chimpanzees and gorillas and do not infect humans. Their prevalence is, therefore, low or non-existent among humans. They have been used to deliver vaccine antigens to humans to test their immunogenicity for viruses and other pathogens, including Ebola, malaria, HIV and hepatitis C.
Viral vectors are not only safe and highly immunogenic, but produce both humoral and high quality T cell responses, which remain active over the long term. The pandemic has further improved the use of this platform, as one of the state-of-the-art vaccines, now being tested 3, is based on one of these vectors.
Engineered Simian Adenoviral Vector
The viral vector GRAd32 is a novel simian adenovirus isolated from a captive gorilla. Like human adenovirus 5, it belongs to group C. When a pilot seroprevalence study was conducted, human adenoviral antibodies were present in 84%, with 68% having significant titers.
The current study used the vector GRAd32 but with different deletions in the genome, in the E1 and E3 regions, while E4 is replaced by the E4 ORF6 of the human adenovirus 5. It also contains an insertion, or the full SARS-CoV-2 – peak length or its stabilized prefusion form, S-2P, which has epitopes recognized by neutralizing antibodies on the tip. Furthermore, this form increases the expression level of the peaks in the transduced cells.
Researchers generated four variants of the candidate vaccine, two based on the full-length peak (wild-type or prefusion) and two on the S-2P protein. These also had only E1 and E3 eliminations or all of the eliminations listed above.
E1 and E3 deletions ensured that the virus was defective in replication and had greater cloning capacity. The E4 substitution was intended to increase growth rates and viral yields in human cell cultures.
The researchers found that both vector spines remained stable over 10 amplification steps, but the substituted type E4 showed a small loss of infectivity. S-2P antigens appeared to be transferred to the cell surface more efficiently than the wild type peak, although both appeared to be produced at equal levels. The S-2P surface binds more strongly to the recombinant soluble ACE2, indicating that RBD is more accessible in the prefusion variant.
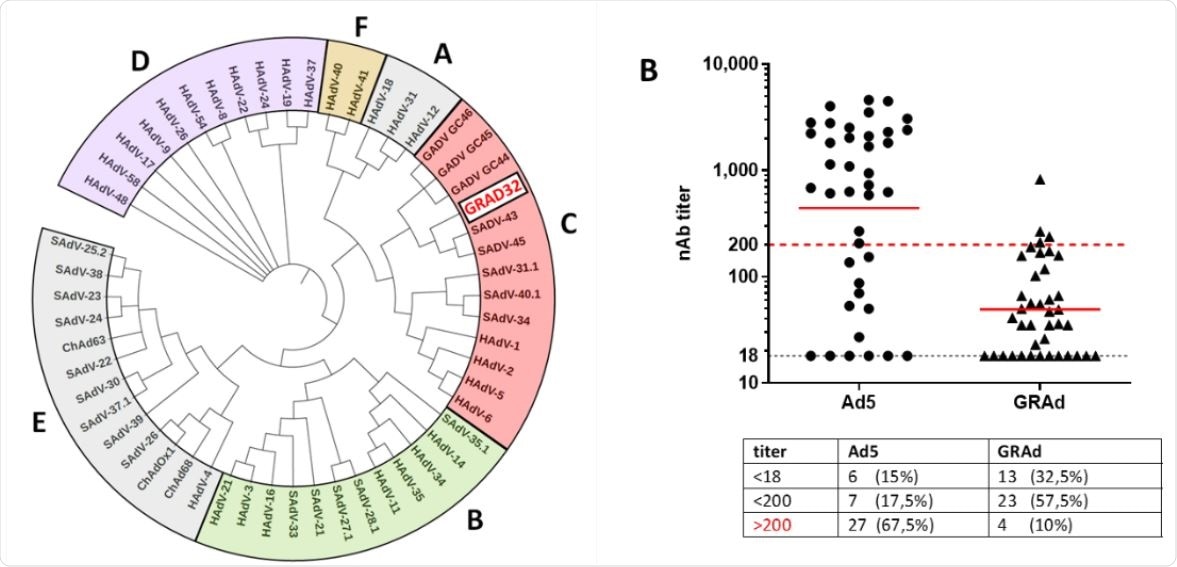
Phylogenetic analysis of GRAd32 and seroprevalence in human sera. A. Phylogenetic analysis using adenoviral polymerase sequences identifies GRAd32 as group C adenovirus. HAdV = Human Adenovirus, SAdV = Simian Adenovirus, GAdV = Gorilla Adenovirus B. Neutralizing antibody titers measured in sera collected from a cohort of 40 healthy human donors . The data are expressed as the reciprocal of the serum dilution with consequent 50% inhibition of the SEAP activity. The horizontal black dotted line indicates the dosage limit value (title 18). The red dashed line indicates a Nab titer of 200, which is reported to have a potential impact on the immunogenicity of the vaccine. The solid red lines indicate the geometric mean. The table shows the absolute numbers and the percentage of sera with NAb titers at Ad5 or GRAd32 below the cutoff value (<18), between 18 and 200 (<200) e sopra 200 (> 200).
Rapid induction of humoral and cellular immunity
Researchers selected GRAd32c-S-2P (GRAd32c contains E1, E3 and E4 deletions with E4 replaced by orf6) for further study due to its higher productivity and better ACE2 binding.
The researchers found that anti-S IgG titers rose rapidly after immunization and increased over time, mainly directed against RBD. Specific T cell responses were also elicited, including those secreting IFN-γ and directed against epitopes on both subunits of the spike protein.
Th1 dominance of the cellular immune response was indicated by the IgG2a / IgG1 ratio greater than 1. This is in contrast to the unbalanced Th2 response obtained with an alum-adjuvanted recombinant S vaccine.
One dose also produced functional neutralizing antibodies that prevented cytopathic effect (CPE) and pseudovirus infection in cell lines. With one dose of the GRAd-COV2 viral vector vaccine in NHP and mice, a Th1 dominant T cell response was achieved, along with neutralizing antibodies to the ACE2 receptor and to SARS-CoV-2. This indicates its promise for further development.
Immunogenicity in NHPs
The benchmarking dose-response immunization study found that at 1×106 viral particles, all animals tested had a detectable immune response. IFN-γ-secreting cells were detected in response, both in the spleen and lungs of the immunized animals.
The researchers then tested the vaccine’s immunogenicity in NHPs to evaluate it in a model relevant to human immunity. They found that prior to the vaccine, all animals had varying degrees of cross-reactive IgG against the peak and RBD of this virus. Specific IgG titers increased after vaccination, to a maximum between the second and fourth week of immunization. After that, it stabilized.
Neutralizing antibodies were rapidly stimulated and reached, albeit at different times in different animals. Neutralization titers remained stable and at week 10 their titers remained comparable or higher than that found in convalescent COVID-19 patients.
Implications and future directions
In light of these findings, the researchers suggest that “a wild-type full-length protein S with proline stabilizing mutations (S.PP) represented the best antigen in terms of immunogenicity and protective efficacy compared to many other forms of S antigen. “
This reflects the higher expression of the pre-fusion peak and the higher neutralizing antibody titer induced compared to the wild-type antigen. A larger study with a viral challenge in NHP is currently underway and should confirm the current findings and evaluate the neutralizing efficacy of the vaccine.
The single-dose regimen has many important advantages when it comes to mass vaccinations. First, these viral vectors induced robust and durable antigen expression in the lymph nodes but reduced innate immunity, unlike the less efficient vectors.
Secondly, this approach allows for rapid increase in production capacities. Overall, these vaccines can allow for modifications using the right cell lines and GMP practices to meet the immense demand for a vaccine around the world.
*Important Notice
bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be considered conclusive, guide clinical practice / health-related behaviors, or treated as consolidated information.
.
[ad_2]
Source link