
[ad_1]

The genes that give the plant’s nucleus its uncovered shape also regulate copper tolerance.
Researchers from the University of Tokyo have identified how cell nucleus architecture can modify gene activity in plants. This discovery reveals fundamental knowledge about genome regulation and points to future methods to potentially manipulate the expression of many genes simultaneously.
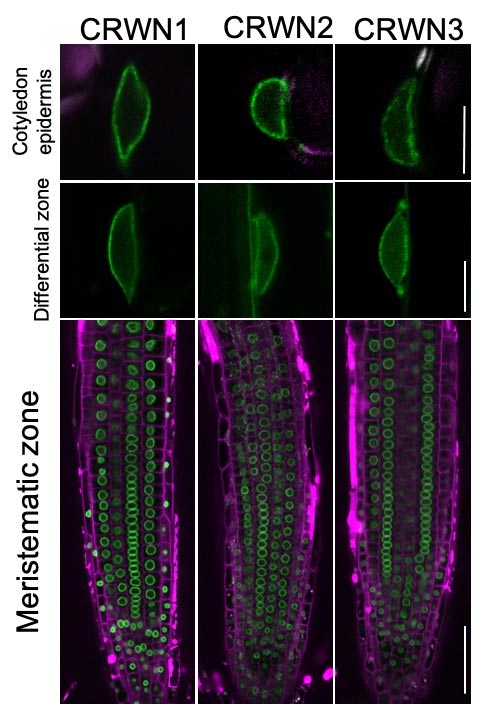
Tokyo University researchers confirmed that crowded nuclei proteins (CRWN1-3) support the oval shape of plant cell nuclei and also play a role in regulating the expression of genes important to cope with environmental stress. . Purple color shows cell walls and green color shows CRWN1-3 in immature leaf (top, cotyledon epidermis), mature root area (middle, differential), and actively growing root ends (bottom, meristematic zone) . Credit: Image by Yuki Sakamoto, CC BY, first published in Nature Communications
The long strands of DNA and the protein mechanism required to activate or deactivate gene expression is contained, floating within the cell nuclei. The nucleus is essentially a sac consisting of a flexible, double-membrane envelope that is supported by a fine-meshed internal frame of proteins called the nuclear lamina.
“DNA does not move aimlessly within the nucleus. We expect there to be non-random spatial positioning of genes around the nuclear lamina, “said Professor Sachihiro Matsunaga who led the research project of the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, recently published in Nature Communications.
Gene regulation is often studied at the one-dimensional level of reading the DNA sequence. Additional layers of gene regulation exist in 3D by changing the shape of the DNA strand. Examples include the epigenetic code that determines how tightly to wrap DNA strands and the phenomenon of “gene kissing”, where distant segments of the DNA strand fold together and change the activity of genes touching each other.
These new findings provide evidence for another 3D method of gene regulation that involves not just the architecture of the genome, but the architecture of its container, the nucleus.
The scientific community has long known that the shape and size of the nucleus can vary greatly during the life of a cell and that these changes can also be programmed as an “internal clock” to determine the age of a cell. However, these discoveries were made using animal cells. Plants do not possess genes that are evolutionarily related to the genes responsible for nuclear lamina in animals.
“Textbooks usually contain some phrases about animal lamina, but nothing to say about plant lamina,” Matsunaga said.
Previous work in 2013 by members of the research team identified a group of four proteins known as CROWDED NUCLEI (CRWN) as the most likely components of the plant’s nuclear lamina.
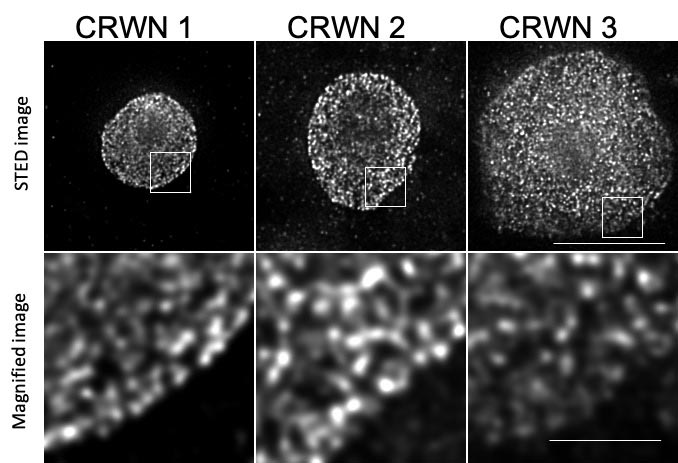
These images of three plant cell nuclei show the web-like web of proteins that make up the nuclear lamina, which supports the shape of the nucleus from within. Tokyo University researchers confirmed that crowded nuclei proteins (CRWN1-3) support the oval shape of plant cell nuclei and also play a role in gene regulation. These images were produced with stimulated emission depletion microscopy (STED), a super-resolution technique. Scale bars = 5 micrometers (top) and 1 micrometer (bottom). Credit: Image by Yuki Sakamoto, CC BY, first published in Nature Communications
To confirm the presence of CRWN proteins in the foil, the researchers first attached fluorescent labels to proteins and nuclei isolated from the root cells of young cress plants, the roadside grass commonly used in research laboratories. Then they measured the position of the proteins in ultra-high resolution microscopy images.
These extremely magnified images show web-like patterns formed by the CRWN proteins around the core shell.
Healthy plant cells have an oval-shaped nucleus, which looks like a large egg in the center of the cell. Genetically engineered plants for CRWN deficiency have smaller, rounder nuclei than normal, probably creating a more crowded environment for the DNA inside.
The researchers then examined the genetically modified plants to see if other genes had different activity levels when the crwn genes were inhibited. More genes known to be involved in the copper response were less active, indicating that somehow the nuclear foil is linked to copper tolerance.

Researchers from the University of Tokyo have identified how cell nucleus architecture can modify gene activity in plants. Plants genetically engineered to inhibit two of the four nuclear lamina-responsible genes (crwn1 / 4 and crwn2 / 3) can survive in low copper conditions (left), but are significantly smaller and weaker in high copper conditions (right) than healthy plants (WT). Credit: Image by Yuki Sakamoto, CC BY, first published in Nature Communications
Plants devoid of CRWN proteins grow shorter than healthy plants even in normal soil. Talle cress with inactive crwn genes planted in soil with high copper levels has become even smaller with a significantly weaker appearance, further evidence that nuclear foil plays a role in plant response to environmental stress.
The researchers also visualized the physical location of copper tolerance genes within the core of both normal and high copper levels. In healthy plants under conditions of high copper content, copper tolerance genes clustered and moved even closer to the periphery of the nucleus. Copper tolerance genes appeared to spread and roam around nuclei in plants with inactive crwn genes.
“If the plant nucleus has distinct regions for active DNA transcription, those regions are likely to be close to the nuclear lamina. This is important and interesting because it is opposite to animal cells, which we know have active regions in the center of the nuclei while the periphery is inactive, ”Matsunaga said.
Most gene editing technologies to increase or decrease gene activity work directly at the one-dimensional level of altering the DNA sequence of the single gene. Understanding how the nuclear lamina affects gene expression could reveal future methods for altering the activity of many genes at the same time reworking the genome and nuclear lamina.
Reference: “Subnuclear Gene Placement Through Lamina Binding Affects Copper Tolerance” by Yuki Sakamoto, Mayuko Sato, Yoshikatsu Sato, Akihito Harada, Takamasa Suzuki, Chieko Goto, Kentaro Tamura, Kiminori Toyooka, Hiroshi Kimura, Yasuyuki Ohkawa , Ikuko Hara-Nishimura Takagi, Sachihiro Matsunaga, 24 November 2020, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038 / s41467-020-19621-z
[ad_2]
Source link