[ad_1]
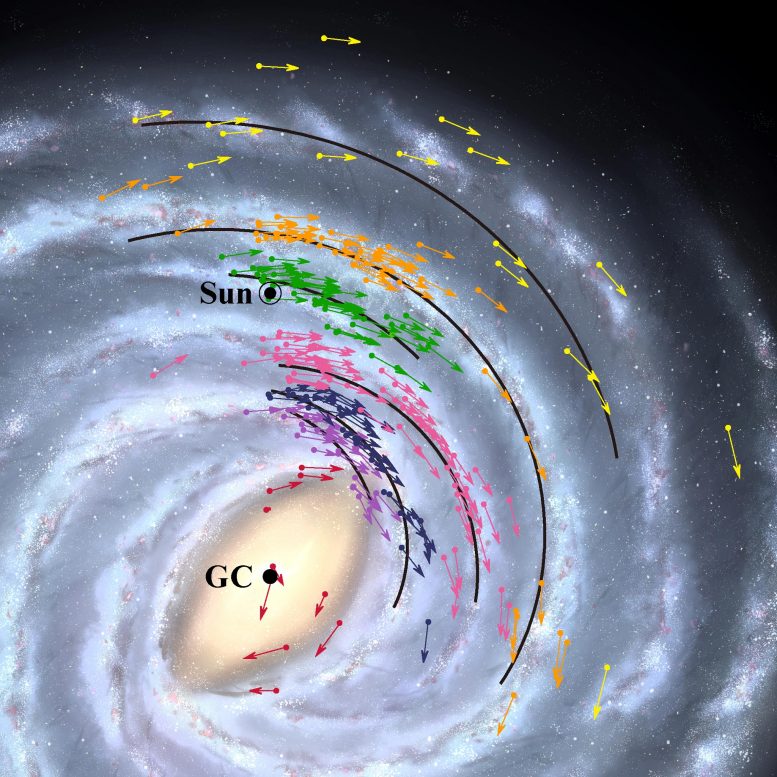
Galaxy position and velocity map. The arrows show the position and velocity figures for the 224 objects used to sample the Milky Way. The solid black lines indicate the position of the curved arms of the galaxy. The colors represent groups of units related to the same arm. The background is a simulation image. Credit: NAOJ
The Earth just got faster at 7km per hour (000 16,000 per hour) and is close to 2,000 light years of supernatural creation. Black hole In the middle of Galaxy Galaxy. But don’t worry, this doesn’t mean our planet is sinking into a black hole. Instead, the changes are the result of better modeling of the Milky Way galaxy based on new observation data, including a list of observations made by the Japanese radio astronomy project Veera over a period of more than 15 years.
Vera (VLBI exploration of radio astronomy, as “VLBI” stands for very long basic interferometry) began in 2000 to map three-dimensional motion and spatial structures in the Milky Way. VERA uses a technique called interferometry to combine data from radio telescopes scattered across the Japanese archipelago to achieve the same resolution as a 2300km-diameter telescope. . Measurement Precision Obtained at this resolution, 10 micro-seconds of arc, placed on the surface of the moon, are in theory sharp enough to resolve a United States coin.
Since the Earth is inside the Milky Way, we can’t go back and see what the galaxy looks like from the outside. Astrology is an important tool for understanding the position of objects and accurate measurements of movements, the overall structure of the galaxy and our place in it. This year, the first Veera Astrometry catalog was released which contained data for 99 objects.
Based on the latest observations from the VERA Astrometry Catalog and other groups, the astronomers created a map of position and velocity. From this map they calculated the center of the galaxy, the point that revolves around everything. The map suggests that the center of the galaxy and the supermassive black hole that inhabits it is 25,800 light-years from Earth. This is closer to the official price of 27,700 light years adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1985. The speed sign on the map shows the Earth traveling at 227 kilometers per hour as it orbits the galactic center. This is faster than the official price of 220 km / s.
Veera now expects to see more objects, especially closer to the central supermassive black hole, to better reflect the galaxy’s orbit and velocity. As part of these efforts, Vera will participate in EAVN (East Asian VLBI Network), which includes radio telescopes located in Japan, South Korea and China. By increasing the number of binoculars and the maximum distance between telescopes, the EAVN can achieve greater accuracy.
Collaboration with VERA and AL’s “First Vera Astrometry Catalog”. Published in August 2020 in the Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan.
[ad_2]
Source link