[ad_1]
Google DeepMind has taken a breakthrough in biology by using artificial intelligence that can accurately predict the ways in which proteins fold.
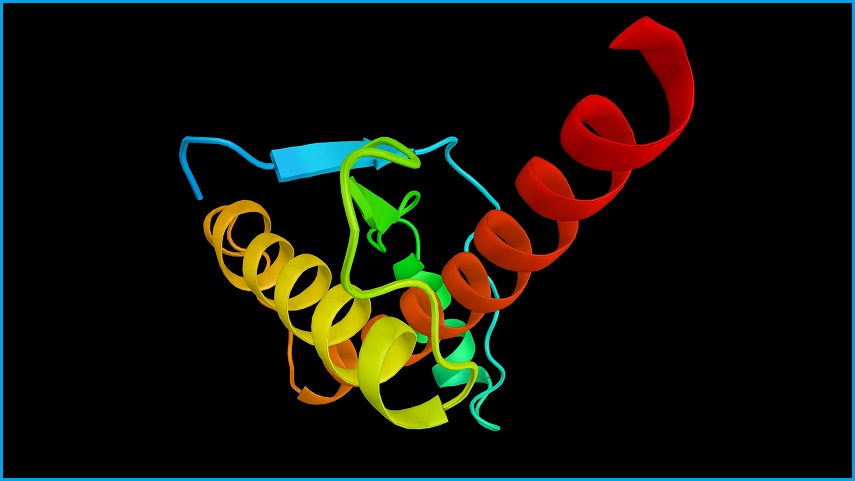
The protein folding problem refers to the high level of complexity involved in how proteins move from simple strings of amino acids to 3D folded structures within cells.
Co-founder of the two-year Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction (CASP) experiment, Professor John Moult, said he was delighted to see DeepMind offer a solution to this long-standing biological challenge.
‘We have been stuck on this problem – how proteins fold – for nearly 50 years,’ said Professor Moult.
“Seeing DeepMind produce a solution for this, having personally worked on this problem for so long and after so many stops and starts, wondering if we would ever get there, is a very special moment.”
DeepMind solved the notoriously difficult problem by using a machine learning system called AlphaFold that was trained on approximately 170,000 protein structures and other large protein sequence databases.
According to the AlphaFold team, training the model took “a few weeks” on 128 cores of Google’s third-generation tensor processing (TPU) unit.
The AlphaFold system can take a sequence of amino acids and produce a highly accurate folded protein.
The breakthrough could have huge implications for biological research and, in particular, for the development of new drugs and medical treatments.
“When DeepMind was started a decade ago, we hoped that artificial intelligence discoveries would one day help serve as a platform to advance our understanding of fundamental science issues,” the AlphaFold team said in a blog post.
“Now, after four years of efforts to build AlphaFold, we are starting to see that vision realized, with implications for areas like drug design and environmental sustainability.”
The director of the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, Professor Andrei Lupas, said Deepmind’s research findings have already shown academic benefits.
“AlphaFold’s surprisingly accurate models allowed us to solve a protein structure that we’ve been stuck on for nearly a decade, relaunching our efforts to understand how signals are transmitted across cell membranes,” he said.
DeepMind became Google’s AI search arm after the tech giant acquired it in 2014.
DeepMind’s research caused a worldwide sensation in 2017, after its self-taught AI Go-playing beat the world’s best player at the ancient board game.
[ad_2]
Source link