 [ad_1]
[ad_1]
A cryptocurrency portfolio is a secure digital wallet used to store, send and receive digital currency like Bitcoin. Most coins have an official portfolio or some officially recommended third-party portfolios. To use any cryptocurrency, you need to use a cryptocurrency portfolio.

Choosing an appropriate cryptocurrency portfolio is the first thing you need to do when you decide to enter the world of cryptocurrency. Just as the fiat currency of the real world is stored in a pocket wallet, your crypto wealth will be stored in a cryptocurrency portfolio. As with your pocket wallet, you want this storage location to be reliable in its ability to hold coins, without it being liable to "lose" your coins (Mt.Gox anyone?). You also want your wallet to be safe, which means that you are the only person able to access and control the funds in your wallet. Portfolios that do not meet these requirements will not be able to store your cryptography satisfactorily. Your cryptocurrency is as secure and accessible as your wallet can be.
Cryptocurrency wallets can be freely compared with e-mail addresses. An e-mail is a digital client that stores your messages; similarly, your cryptocurrency portfolio is a digital client that stores cryptocurrency. Your e-mail has an address and a password that allows you to access it and send / receive messages. Comparable to this, a cryptocurrency portfolio has a public key that functions as an address on which it is possible to send cryptocurrency and a private key that allows access to its own funds and should only be known
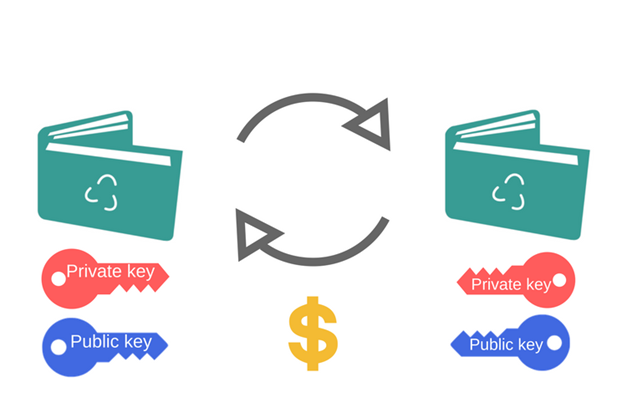
Source: https://blockgeeks.com/guides/cryptocurrency-wallet-guide/
Someone who is sending you cryptocurrency is basically making a digital statement that you are now the owner of the assigned tokens. The sender will send the cryptocurrency creating a transaction that lists the public key of your portfolio as a recipient of funds. Once these funds are received, their new owner must have the private key corresponding to the public key to access these funds. If the public and private keys match, the balance in the digital wallet of the receiver will increase and one in the sender's portfolio will decrease accordingly. Actual coins are not exchanged when the transaction is registered via a blockchain entry and a change of balance on the cryptocurrant portfolios involved.
Hot Storage vs. Cold Storage

Source: https://bitcoinira.com/articles/hot-wallets-vs-cold-wallets[19659012] A distinction must be made between all available portfolios out there: these portfolios can be defined as hot storage and cold storage portfolios.
Wallets with a warm shelf are similar to carrying around a wallet in a pocket. Funds are stored on a device that has a direct connection to the Internet, allowing for greater liquidity and the ability to immediately access cryptographic funds to make payments. Online wallets, wallets, exchange portfolios all fall into this category. While these portfolios simplify the transaction process, they increase the risk of being violated. Malware attacks and compromised centralized server exchanges have been responsible for significant cryptocurrency losses in the past, with the Bitfinex and Bitgrail hacks that were the best (or perhaps the most suitable to say the worst) examples of this.
🏆 Learn how you can create a paper wallet – click here to learn more about cryptographic portfolios .
To their opposites we have cold preservation portfolios . These portfolios do not have a direct connection to the Internet and are much safer than their hot counterparts. Their risks are mostly related to the fact that the storage device is damaged or lost and not a single cold wallet has been reported as hacked so far. Since they provide a large security network from hackers, people who are trying to maintain a cryptocurrency for a longer period of time should find them as the best option. However, they have the disadvantage that funds are not easily accessible, even for the owner himself, making them a bad choice if you want to make daily exchanges or make instant cryptographic payments. Sometimes they can also be a bit difficult to configure correctly. These portfolios include paper wallets and hardware wallets.
How many types of cryptocurrency portfolios are actually available?
Any cryptocurrency portfolio is a combination of the private key and a public key / address to which criptovaluta can be sent. Currently there are numerous cryptographic portfolios, each with its own unique characteristics and defining elements. And even if there are no two identical portfolios, we can divide all existing clients into five general types:
-
Hardware Portfolios
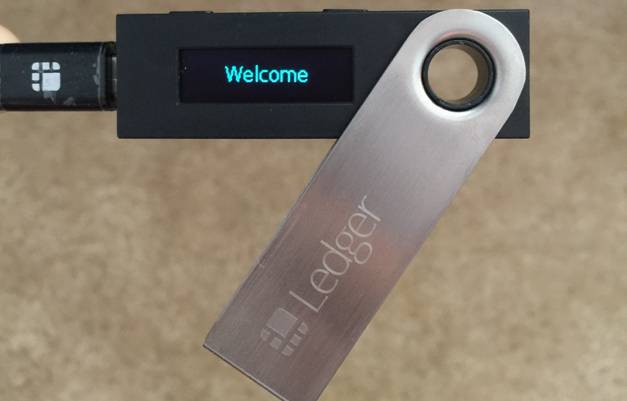

Hardware portfolios are a type of cryptocurrency wallet that stores users public and private keys on a secure hardware device. These devices are typically pocket-sized and can be connected to a computer via a USB cable. Before accessing your hardware portfolio, sometimes you will need to install proprietary software on your computer. They are compatible with various PC interfaces and can support one or more cryptocurrencies. Some of the most advanced hardware portfolios contain up to 20 tokens that, when considering the total amount of cryptocurrencies available, are not many at all.
Some portfolios are software-free and require the installation of a complete update of the wallet software version on the device, which protects it from being tampered with by the seller / seller. Some have screens and buttons that help you manage your wallet without a connected computer. Accessing a hardware portfolio is usually no more difficult than connecting it to a computer and inserting a pin.
🏆 Are you looking for a mobile ethereum wallet? Read this.
Hardware portfolios keep your private keys stored in an offline environment, away from vulnerable devices connected to the Internet. Because the keys are generated on the device, they are completely protected, even when you connect the device to a computer infected with malware (which does not mean you should do it). Even if you lose your hardware portfolio, anyone who finds it will need to know the PIN to access the funds on it. You are given an option (which you should absolutely use) to create a backup code for your hardware portfolio, which allows you to create a copy of your wallet and recover your cryptocurrency if you lose the hardware device itself.
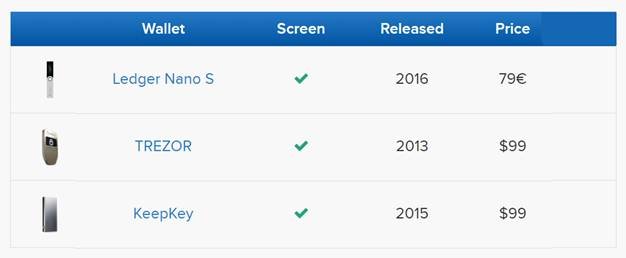
Anyone looking for long-term "Hodling" should try to invest in a hardware portfolio. These devices are not free; their cost ranges from $ 70 to $ 150 dollars, sometimes even more. Despite being the most expensive form of wallet, they provide the safest option for storing cryptocurrency. At the time of writing this article no cryptocurrency cases were reported stolen from someone's hardware portfolio. Being safe involves a cost in terms of limited liquidity and accessibility of funds. The most famous hardware portfolio options are Ledger Nano S, Trezor and KeepKey.
Pro:
- Extremely safe way to archive cryptocurrency
- Easy backup
- Easy installation, even for encrypted newcomers [19659032] Cons:
- They are not free
- Could be lost because it tends to happen with small physical objects
- Funds are not easily accessible
-
Paper wallets
 [19659004] Paper wallets are a little more technical and difficult to install and therefore are not suitable for the most demanding beginners in the encrypted world. However, anyone who wants to learn and employ a little caution should not have major problems creating one. There are many online tutorials that explain in detail how to properly set up a wallet for cryptocurrency. A paper wallet is often presented as the safest way to store cryptocurrencies, and this is not without a good reason.
[19659004] Paper wallets are a little more technical and difficult to install and therefore are not suitable for the most demanding beginners in the encrypted world. However, anyone who wants to learn and employ a little caution should not have major problems creating one. There are many online tutorials that explain in detail how to properly set up a wallet for cryptocurrency. A paper wallet is often presented as the safest way to store cryptocurrencies, and this is not without a good reason.
🏆Read here the best DASH wallets.
An owner of a typical paper wallet can simply print his private keys and public addresses on a piece of paper and start transferring his cryptocurrency onto it. This portfolio keeps your private keys offline and offers security similar to a hardware portfolio. The keys are printed as QR code that can be scanned to complete the transactions. All a user needs to do is worry is how to take care of a piece of paper. Paper wallets are classified as cold stores, as they clearly have no access to the Internet.
Some risks derive from these portfolios. Your card can be stolen or someone can take a picture of your keys. The printer you use to print your keys may not work well or it may be inkjet (which never works well, does it?). Finally, the paper is very fragile and can be damaged by water, fire or heavy use. We recommend that a user create multiple copies of his keys to avoid losing his wallet. One way to circumvent the fragility of paper is the use of wallets that are etched on metal plates. Although they are much more durable, they can still be subject to natural elements and wear and tear
Pros:
- Easy to use and store
- Easy to replace a lost wallet
- Extremely safe
Cons:
- Easy to lose / damage
- Difficult to configure
- Low liquidity of funds
-
Wallets for desk

Wallets for desk are wallets which can be downloaded and stored on your computer. They are basically software that supports cryptocurrency storage and transaction; most can be downloaded for various operating systems like OSX, Windows and Linux.
Desktop wallets store your public and private keys on the device where the software is installed, which is your PC. This means that your funds are as secure as the PC itself. If you install a desktop wallet on a PC that is used for daily Internet browsing, with a powerful firewall, anti-malware and anti-virus software is highly recommended.
PCs are usually connected to the Internet, which means that wallets are considered hot storage. Therefore, it is advisable to keep only small amounts of funds on these portfolios. Since your average PC is not exactly very mobile, most people use desk wallets for trading and home purchases. Sometimes people use desktop wallets as cold storage by installing proprietary software on computers that are not constantly online. These devices are not used for daily navigation and will only be connected to the Internet to update the balance or execute transactions.
There are many desktop portfolios available on the market and products such as Electrum, ArcBit, Exodus and Bitcoin Core are some of the most popular
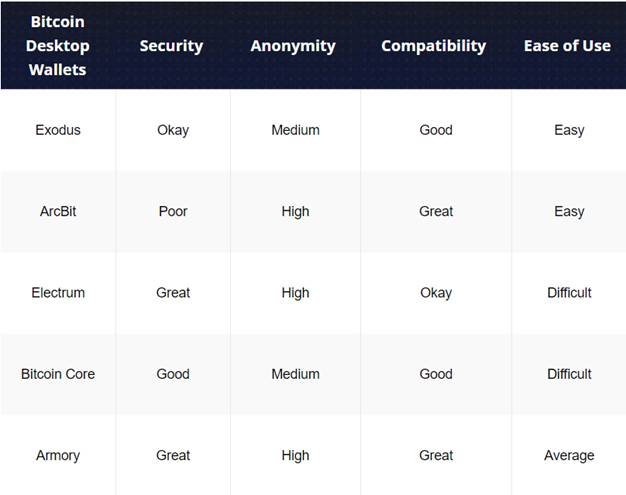
Source: https: / /coinwriting.com/bitcoin-desktop-wallet/
Pros:
- Easy to use
- Wide availability and free
- Safe with due caution
- High liquidity
- Keys stored on the device
Cons:
- Less secure when connected to the internet
- Requires Internet connection to synchronize with the blockchain
- Hardware failures can lead to a loss of funds
-
Wallet mobile

Mobile wallets are software applications that can be downloaded via an app store and installed on your mobile device. Both Apple stores and Google Play offer a wide variety of mobile wallet clients. It is interesting to note that in 2014 Apple filed the cryptocurrency portfolios, but has since abolished the restrictions. Mobile wallets are usually much smaller and simpler than their desktop siblings, mainly because of the limited storage capacity of mobile devices.
With mobile wallets, your keys are stored on the device itself. Although it is better than storing them online, there may still be a problem if you lose your phone. These portfolios can be restored with the help of a wallet suit originally used to generate the wallet keys. Mobile phones are also sensitive to malware and viruses, perhaps even more than PCs due to the bare nature of mobile security software. Because each phone is almost constantly online, these portfolios are considered hot storage.
🏆Here is our list of the best litecoin portfolios.
Mobile portfolios usually have active and large development communities, as it is relatively easy to start programming Android / IOS platforms. Funds on a mobile wallet are easily accessible and can be transferred with a few clicks of the button. Some of the most popular mobile wallet clients are Mycelium, Coinomi, Electrum, breadwallet, Edge, Bitcoin Wallet etc.
Pros:
- Lightweight and easy to use
- Widely available and free
- Good back-up options
- High liquidity of funds
Cons:
- Your mobile device can be easily lost
- It is not the safest option for long-term archival
- Sometimes questionable quality of development and coding
-
Portfolios online
An online wallet is a wallet that runs in the cloud and accessible via a web browser such as Chrome or Opera. Web portfolios are managed by a third party, which means that private / public keys are stored on the service provider's servers. This makes these portfolios light and easily accessible, as the user is not required to download a huge client.
The advantage of online portfolios – apart from the general simplicity – is the ability to merge transactions together before pushing them onto the blockchain. This can significantly reduce transaction fees. They can also make internal transfers at zero rates. This creates a payment ecosystem within the payment ecosystem that can attract customers and increase the user base with its benefits.
Third-party storage allows faster service but at the same time means that users do not have control over their private keys. The third party who holds your keys is entirely responsible for the integrity of your wallet and you must trust them that they will not run away with your money. This third part will store the user's keys on a centralized server, which means that a server hack could expose a huge amount of funds to malicious players. Gox, Bitstamp and Bitgrail have shown the cryptic world the dangers of centralized key storage. One other vulnerability of these centralized services are DDoS attacks that can slow down servers and cause a negative user experience.
Online portfolios are displayed as exchange portfolios or as separate third-party portfolios that can store funds. While each exchange offers its own portfolio, the most cited third-party portfolios include Green Address, BitGo, Coin.Space, Coinapult, MyEtherWallet, Metamask etc.
Pros:
- Maximum liquidity
- Low fares
- Reduced storage space required
- Multi-platform access
Cons:
- Minimum security
- Third-party control on private keys
- May slow down in case of intensive use
The writers and authors of CapitanAltcoin may or may not have a personal interest in any of the projects and activities mentioned. None of CaptainAltcoin's content is an investment advice nor a replacement for the recommendations of a certified financial planner.
[ad_2]Source link