 [ad_1]
[ad_1]
Trading on futures is a common practice in the cryptocurrency space, with futures exchanges on CME and CBOE for futures on Bitcoin, and among the most encrypted BitMEX is among the most important exchanges.
What are Bitcoin and Crypto Futures?
Encrypted futures are a way to exchange future action on prices for cryptographic assets. Bitcoin futures are the most common future encrypted, affecting the mainstream financial world at this time last year.
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) traded futures trading products with Bitcoin liquidated in cash last December. Cash-settled means that these futures are not supported by real Bitcoin. When futures contracts expire, the value is paid to the merchant in cash instead of Bitcoin.
The Trade Station online broker explained the futures contracts in an easy way. They are "an agreement to make or take a commodity or a financial instrument on a date set in, you guessed it, the future."
Each futures contract contains a specified amount of the exchanged product. In the case of Ccoe Bitcoin futures, each futures contract contains a Bitcoin and is adjusted based on Gemini's Crypto exchange price for Bitcoin.
These futures contracts (in this case, Bitcoin) can be purchased or sold at the discretion of the trader at any time during the contract period, as the offer and the market demand determine the price of the contract and the underlying asset. (Bitcoin).
Thus, as a trader or market price speculator, futures allow "to take positions on futures, along with their risks and opportunities, without ever having to take over the underlying asset," as explained by Trade Station.
How does futures trading work?
On the CME or the CBOE, traders can earn or lose money by speculating on the price of Bitcoin, without actually buying or holding the underlying asset.
The purchase of Bitcoin Futures (also called "going long" or "longing")
A significant part of futures trading involves trading these contracts several times between the expiration of the contract and the expiry of the contract. Bitcoin futures trading often involves a constant adaptation to the changing sentiment of the market, to the purchase and sale of contracts based on Bitcoin spot price as a result.
For example, suppose a trader named Dave decided to exchange those monthly Bitcoin futures several times during November 1st – 1 Decemberst contract period (fictitious for this example). Dave could essentially buy a position in future contracts on Bitcoin at any time during this time at the market price (the price of Bitcoin at the time of purchase) and then sell at any time before December 1st maturity, seeing profits or losses based on Bitcoin spot price. Dave would be paid in cash depending on the result of profits or losses.
A specific example of a trade that Dave could take could see it buy a Bitcoin futures contract for $ 3,100 on November 8thand then selling on November 10thth for $ 3,200 (if the spot price of Bitcoin has risen so much over that time period), seeing a profit of $ 100, paid in cash. Although the price went from $ 3,100 to $ 2,900, and Dave sold the contract at $ 2,900, he would only receive a $ 2,900 payment, with a $ 200 loss.
Sale of Bitcoin Futures (also called "short" or "shorting")
Dave also has the option of selling Bitcoin futures. This basically means betting that Bitcoin will fall in price in the future. When Dave sold a futures contract on Bitcoin, it means that he borrows a future Bitcoin contract from someone else on the exchange and sells it, hoping to buy back the contract at a lower price and keep the price difference. This is done by the exchange, so traders do not have to look for individual contracts to borrow and then return later.
For example, if the spot price of Bitcoin is $ 3,000 on November 3rdrd and Dave thinks it will fall to $ 2,000 by November 18thththen it would sell a short-term contract on Bitcoin futures using the CME or CBOE exchange features. If Dave sold a Bitcoin futures contract for $ 3,000 on 3 Novemberrdand the price fell to $ 2000 on November 18thth, repurchased the contract and received a cash payment of $ 4,000 (his initial $ 3,000 plus a profit of $ 1,000).
In the same short commercial example, once Dave has entered his short position at $ 3,000, he would be able to close that position at any time, until December 1stst deadline. So if Dave sold a short contract for $ 3,000 on 3 Novemberrdand Bitcoin's spot price fell to $ 1,500 on November 8thth, Dave could regain that contract position at his discretion, ending the trade and taking home a profit of $ 1,500. On the other hand, if Bitcoin's spot price rose to $ 4,500, and Dave chose to close the transaction, he would terminate the contract and lose $ 1,500.
What is the expiration and settlement of the contract?
Contract expiry is the date on which future contracts expire and the trading activity ends. "Before the expiration date, traders have a number of options to close or extend their open positions without keeping the trade until maturity, but some traders will choose to keep the contract and go to regulation," explained the CME Group on their website.
The regulation of the contract also occurs on a specific date. The CME group explained that the regulation is "the fulfillment of the legal delivery obligations associated with the original contract". Therefore, on the specified date, the underlying asset amount would have been given to the contract holder, at the market price at the time of settlement.
Because the CMC and CBOE Bitcoin futures are settled in cash, the contract holder will receive the fiat value (USD, etc.) of the contract price at the time of settlement. For more information: CME Bitcoin futures settlement dates.
Will future settlements have an effect on the price of Bitcoin?
Global stock futures, such as the NASDAQ, have effects on the markets. Therefore, it is widespread to think that the Bitcoin futures of CME and CBOE have the same impact on the price of Bitcoin.
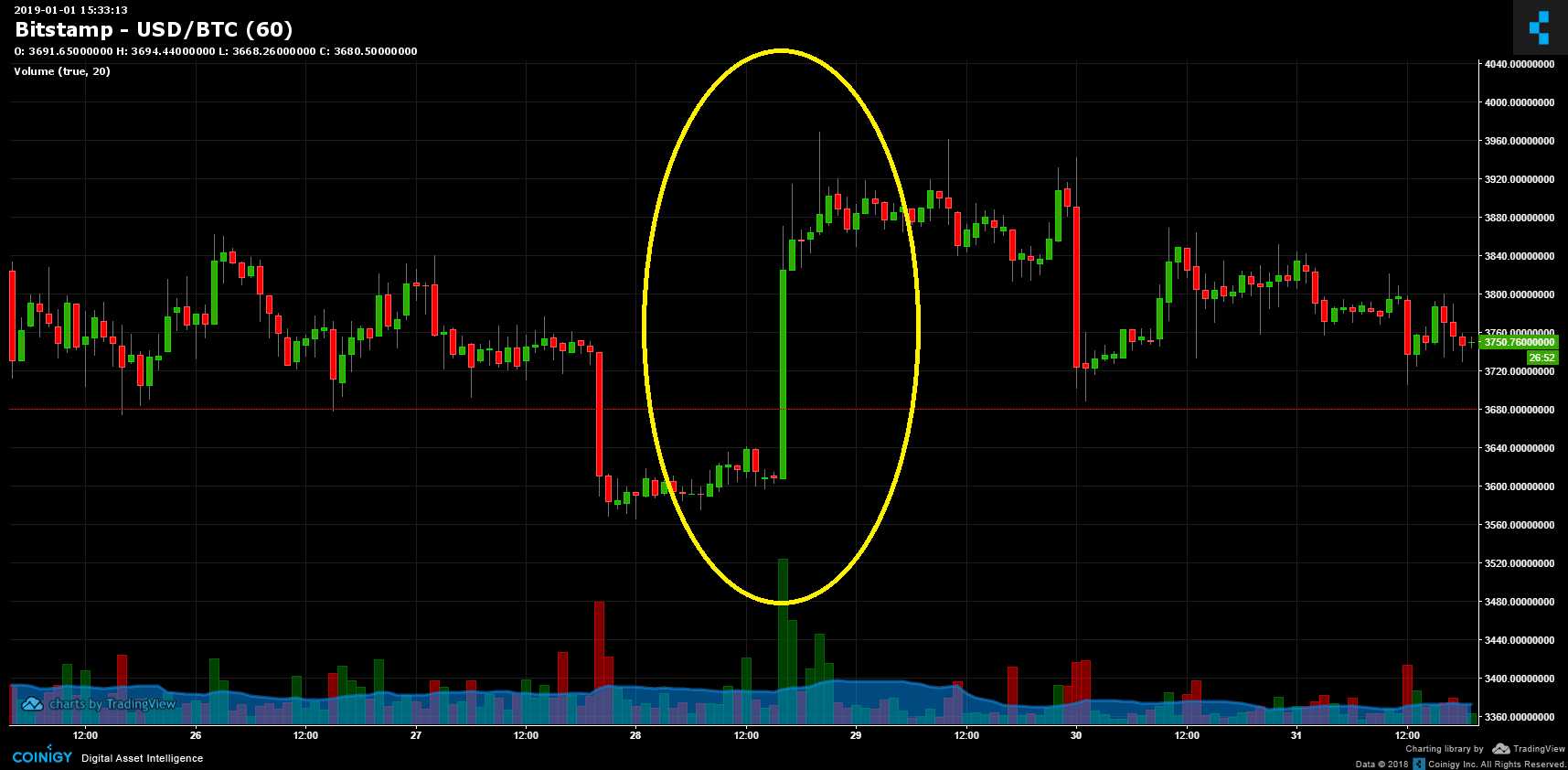
This is sometimes true. Looking at the Bitcoin chart, compared to the futures settlement dates, often there was a price action that is probably in advance of the liquidation event, but as you'll see, not always c & a # 39; is such an action.
The following chart shows the price of Bitcoin before June 29 (2018) Six-month ECE with Bitcoin futures. 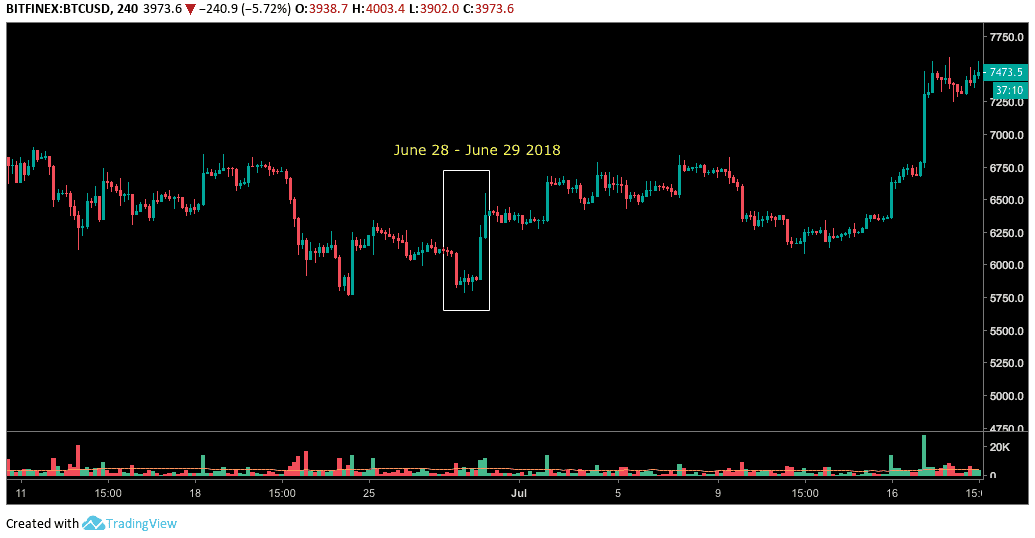
We can also see the action of Bitcoin prices during the last agreement on futures on 28 December 2018:
Unlike the June and December payments, futures established in September 2018 had shown minor fluctuations in Bitcoin.
To summarize the effects, although this could also be just a coincidence, we can probably assume that the future agreements of CME and CBOE influence the price of Bitcoin.
Bitcoin and Altcoin Future Contracts of BitMEX
Unlike CBOE and CME, BitMEX futures are encrypted, which means that the underlying cryptographic activity is delivered when the contract is terminated.
BitMEX has recently announced the addition of numerous new cryptographic futures futures lists, combined with Bitcoin. "The 17thth In December 2018, the quarterly futures contracts will be listed: ADA (Cardano), BCH (Bitcoin Cash), EOS (EOS), ETH (Ethereum), LTC (Litecoin), TRX (Tron) and XRP (Ripple) of March 2019 ", BitMEX he stated in a recent blog post.
Because these contracts are combined with Bitcoin, their value is evaluated based on their Bitcoin value. The contractual dimensions for these new contracts are a currency of the specified good (1 ADA, 1 EOS, etc.). For example, an EOS token is roughly equivalent to 0.000685 BTC (value at time of printing). The mentioned futures contracts speculate on the Bitcoin value that these new assets will have at the time of the quarterly expiry.
BitMin Biturein Perpetual Futures
BitMEX is famous for these perpetual contracts. Each contract equates to $ 1 USD, with no expiration or expiration date. With these perpetual exchange contracts, traders can trade in and out of positions as many times as they wish, without having to take note of expiration dates, as in the case of the CME and the CBOE. BitMEX allows its traders to take advantage of up to 1: 100. For more information, visit the BitMEX CryptoPotato for Beginners and Advanced Guide.
However, these perpetual term contracts have something called funding, which occurs every eight hours and can have an impact on profit or loss. "You will pay or receive funding only if you maintain a position at any of these times. If you close your position before the exchange of funds, you will not pay or receive any funding," explained BitMEX on their site.
In short words; the loan consists of an interest rate and a premium or discount. "This rate aims to keep the traded price of the perpetual contract in line with the underlying reference price.This way, the contract mimics the way the commercial margin markets work as buyers and sellers of the contract periodically exchange payments from interests. "
Bitcoin and Crypto Trading Futures: pros and cons
Professionals
– The option to bet against the market: futures are either way. So, you can shorten your favorite cryptocurrencies.
– Lever trading: futures allow you to take advantage of your capital. This can also be another advantage for cryptography-based exchanges, because there is always the risk of keeping cryptography on exchanges (for security reasons).
– Coverage: from the aforementioned reasons, futures trading is an excellent way to cover any portfolio. Instead of selling your BTC, you can buy some short futures to cover your wallet during a bearish market like the one we had in 2018.
Versus
– High risk: futures are considered the highest risk trading instruments. Pay attention to the settlement price that the amount of the guarantee allows you.
– Tighten can kill: sudden short or long pressures can turn a profitable position into a bleeding loss at the same time. In the crypt, squeezing and manipulation are part of the game.
– High volatility: on the one hand volatility is a paradise for traders; on the other hand, volatility sometimes makes it difficult to determine the sentiment of the market.
– Commissions: borrowed money is never free, sometimes taxes are expensive. The taxes differ for the exchange.
CryptoPotato video channel
More news for you:
[ad_2]Source link