[ad_1]
[ad_1]
It may seem like a broken record at this point, but yet another decentralized finance protocol (DeFi) has been exploited recently.
And, once again, the exploit happened on a competitor of Yearn.finance (YFI).
Here’s more on what happened and what DeFi users can do to prevent their funds from being attacked in the future.
Yearn.finance’s ValueDeFi fork was hacked for $ 7 million
In August and September, the Yearn.finance fork was all the rage. Yearn.finance had quickly become the cryptocurrency industry’s treasure trove, with $ 1 billion in deposits and its native YFI token with a market cap of $ 1 billion.
Forks on forks were released.
One fork that gained traction was YF Value (YFV), which, like Yearn.finance, was marketed as a place for users to deposit cryptocurrencies and earn a steady and secure return. While extremely similar in concept to Yearn.finance, the marketing strategy worked: at its peak in early September, YFV had a market capitalization of just $ 150 million.
Unfortunately, YFV isn’t as safe as first thought.
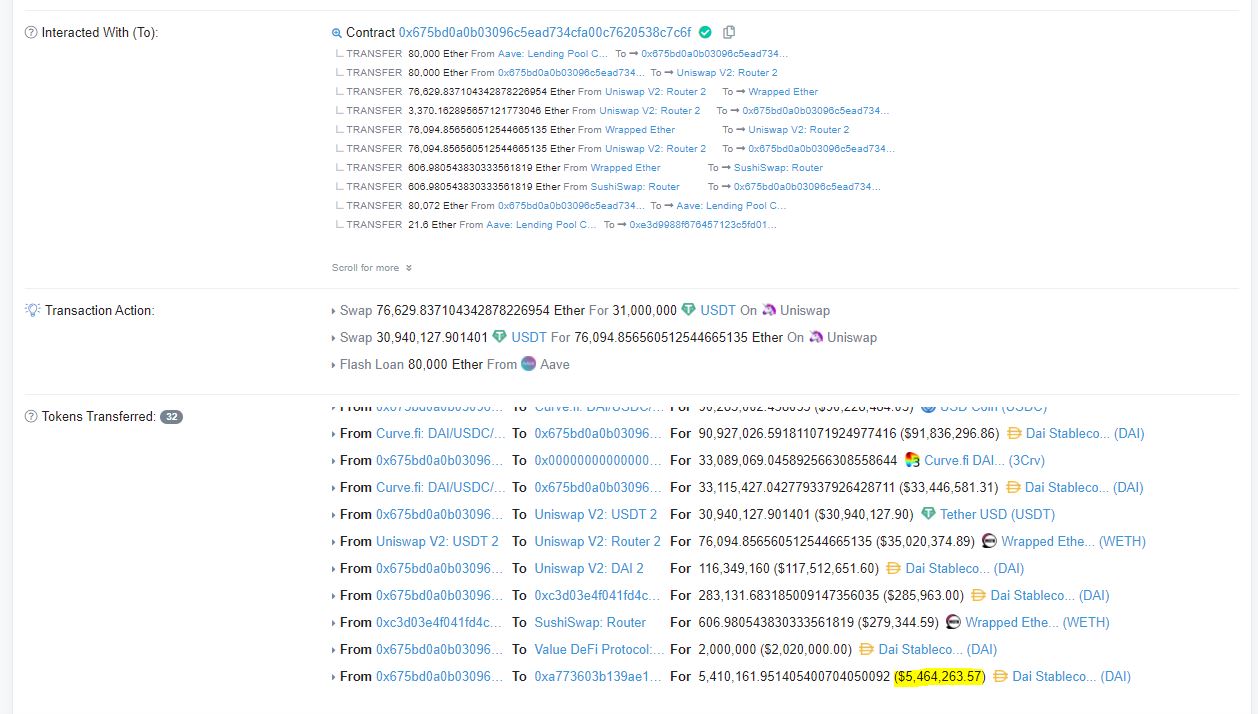
On Saturday morning, users began taking notice of a large Ethereum transaction involving Aave, Curve, Uniswap and YF Value (now known as Value DeFi).
In that transaction, a user had withdrawn 80,000 ETH from Aave in a flash loan, along with another $ 116 million in DAI from Uniswap.
These funds were later traded to manipulate the price of stablecoins on Curve. This manipulation meant that the attacker was able to obtain value storage tokens that were worth more than the actual value of the stablecoins that underpin those tokens.
In total, $ 7.5 million of DAI was drained from Value, although $ 2 million was returned to the protocol by the attacker’s pseudonym.
While unfortunate for depositors, literally hours before the attack, Value billed itself as “the safest and most advanced technology in the DeFi space,” claiming that its developers represented the well-known flaws in Ethereum’s smart contracts.
13 hours ago:
– Value DeFi calls itself “the safest and most advanced technology in the DeFi space”10 hours later:
– The flash loan was attached for $ 7 million pic.twitter.com/yYbWuYBX03– Spencer Noon (@spencernoon) November 14, 2020
Value’s exploit comes after similar attacks took place with Akropolis and Harvest Finance.
Avoid protocols with poor Oracle integration
At the heart of many of these exploits and potential attack vectors is the lack of proper Oracle integrations. An oracle is software that provides data outside of a system to that system; in DeFi, oracles are often used by protocols that need to know the price of a cryptocurrency.
“Honest” oracles use a variety of metrics, such as using an index or taking a snapshot, to mitigate the risk of price manipulation attacks.
The protocols that were exploited by the flash lending attacks did not use properly integrated oracles, allowing inter-block prices of stablecoins to be manipulated for the benefit of the exploiters.
Do you like what you see? Sign up for daily updates.
[ad_2]Source link